Category: 2D Symbologies
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Data Matrix (also known as DataMatrix or GS1 DataMatrix) is a compact, high-performance 2D barcode made up of black and white modules arranged in a square or rectangular grid.
Data Matrix codes can store a large volume of data in a small physical space, have robust error correction capabilities, are adaptable in physical size, and support variable-length data content and different character encoding schemes.
They are used in the logistics, manufacturing, healthcare, defense, retail, and electronics industries. This comprehensive guide provides a technical walkthrough of everything you need to know when building applications that create or decode Data Matrix barcodes. 
What is a Data Matrix code?
A Data Matrix code is a two-dimensional barcode that encodes variable-length data and stores a large amount of organized information (the data structure) in a small graphical space (the data carrier).
The difference between data carrier and data structure
A data carrier is a graphical representation of data in a machine-readable form, while a data structure is the data format that is encoded within the carrier.
There are several versions of the general Data Matrix technical standard that define industry-agnostic data carrier and data structure specifications. This guide is based on the newest and most commonly used version, ECC 200, which is defined in ISO/IEC 16022:2024 — Data Matrix bar code symbology specification.
The most commonly used implementation of the Data Matrix structure is defined by the GS1 DataMatrix guidelines recognized by the ISO/IEC. While it’s possible to use a non-standard structure inside a Data Matrix symbol, most industries follow the GS1 DataMatrix guidelines. The concepts and examples presented in this guide cover these guidelines.
Try the Scandit Barcode Scanner SDK
Evaluate Data Matrix decoding with a 30-day free trial.
How a Data Matrix code works
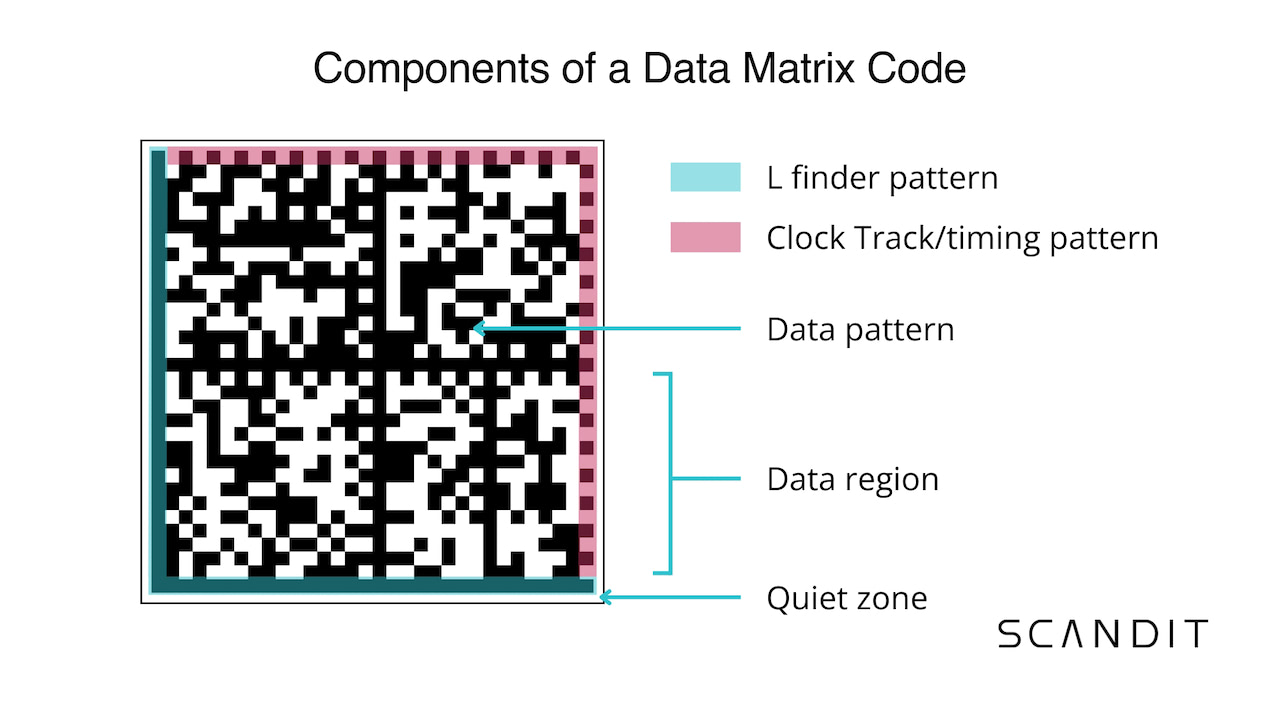
A Data Matrix code has three data carrier components:
- A finder pattern with two parts forming the perimeter of the symbol. The first is a solid L-shaped line, known as the “L finder pattern,” that defines the size (rows and columns), orientation, and distortion (skew) of the symbol. Second, a dotted L-shaped pattern opposite the L finder pattern, known as the “Clock Track” or “timing pattern,” further defines the symbol's structure.
- A data pattern encoded as a series of rows and columns of byte characters within the finder pattern. This is also broken into one or more data regions that organize information. For example, the image below has four data regions. Additional finder patterns border each data region.
- A quiet zone that defines a graphic-free area surrounding the symbol, to help scanners distinguish between the code and background.
How does Data Matrix code size affect data capacity?
The size and data capacity of a Data Matrix code are related to the symbol’s shape (square or rectangular) and the format of the encoded data. The following table, adapted from the GS1 guidelines, shows the storage sizes and the total number of possible size combinations:
Form | Maximum characters (alphanumeric) | Maximum characters (numerical) | Number of rows (min…max) | Number of columns (min…max) | Number of possible symbol sizes (e.g., 10x10, 12x12, etc.) |
Square | 2,335 | 3,116 | 10…144 | 10…144 | 24 |
Rectangular | 71 | 96 | 8…16 | 18…48 | 6 |
This table shows the number of data regions based on the symbol’s size:
Total symbol size | Number of data regions |
Square | |
10×10 to 26×26 | 1 |
32×32 to 52×52 | 4 |
64×64 to 104×104 | 16 |
120×120 to 144×144 | 36 |
Rectangle | |
8×18 | 1 |
12×26 | 1 |
16×36 | 1 |
8×32 | 2 |
12×36 | 2 |
16×48 | 2 |
How is data encoded in a Data Matrix symbol?
Data Matrix supports various data encoding schemes, such as ASCII, C40, X12, EDIFACT, and Base 256.
The GS1 DataMatrix standard mandates encoding to be a subset of ISO/IEC 646 (equivalent to ASCII table 256). However, most real-world applications use UTF-8 encoding for its variable-length scheme and broader range of characters.
The data strings in a GS1 Data Matrix symbol include these characters:
Function 1 Symbol Character (FNC1) | Application Identifier (AI) | Element strings |
Identifies the type of ISO/IEC Data Matrix symbol. For GS1 DataMatrix, the FNC1 is ]d2. | 2, 3, or 4-digit numbers that define the meaning and format of the subsequent data. For example:
See GS1 Application Identifiers for the complete list. | The variable-length, item-specific data. |

The Data Matrix code to the right has the data string ]d2013456789012345615251231. This breaks down into three components:
- ]d2: Function 1 Symbol Character (FNC1) identifying this as a GS1 DataMatrix code.
- 01 34567890123456: Application Identifier (AI) defining this as a Global Trade Identification Number (GTIN), and the GTIN of the product.
- 15 251231: Application Identifier (AI) defining this as a best before date, and the date in a YYMMDD format.
Data Matrix error correction
GS1 DataMatrix employs the Reed-Solomon error correction method, which is integrated into the symbol itself. This technique adds complementary data patterns during symbol creation, allowing for the reconstitution of corrupted data. Data Matrix codes remain scannable through this mechanism even if up to 30% of the code area is damaged.
The space required for error correction codes depends on the size of the symbol. For example, a 10×10 symbol has 62.5% of its data used for error correction, while a 144×144 symbol has 28.5% consumed.
What is structured append in a Data Matrix barcode?
“Structured append” is a Data Matrix feature that allows data to be split across multiple symbols that are scanned and reassembled by scanning software. Defined in ECC 200, this feature is set by a special element in the data pattern (233) and allows up to 16 separate but logically linked symbols.
Reading data encoded using structured append requires a barcode scanner that supports the feature, can scan multiple labels at once or in rapid succession, and aggregates the individual symbol data.
Where is a Data Matrix barcode used?
Due to their high data density, Data Matrix barcodes are ideal for situations that require large volumes of data encoded in a small space, such as logistics packages, manufacturing parts, healthcare products, and retail items. Application examples include:
- Small electronic components where tiny barcodes must be used to fit the product. For example, the US Electronics Industries Alliance (EIA) recommends labeling components using Data Matrix barcodes in its CEA-706, Component Marking Standard.
- Healthcare, where Data Matrix is the only 2D barcode endorsed by GS1 Healthcare for product identification in support of traceability, pharmacovigilance, and post-market surveillance.
- The US Department of Defense uses Data Matrix to track equipment under its Item Unique Identification (IUID) requirements.
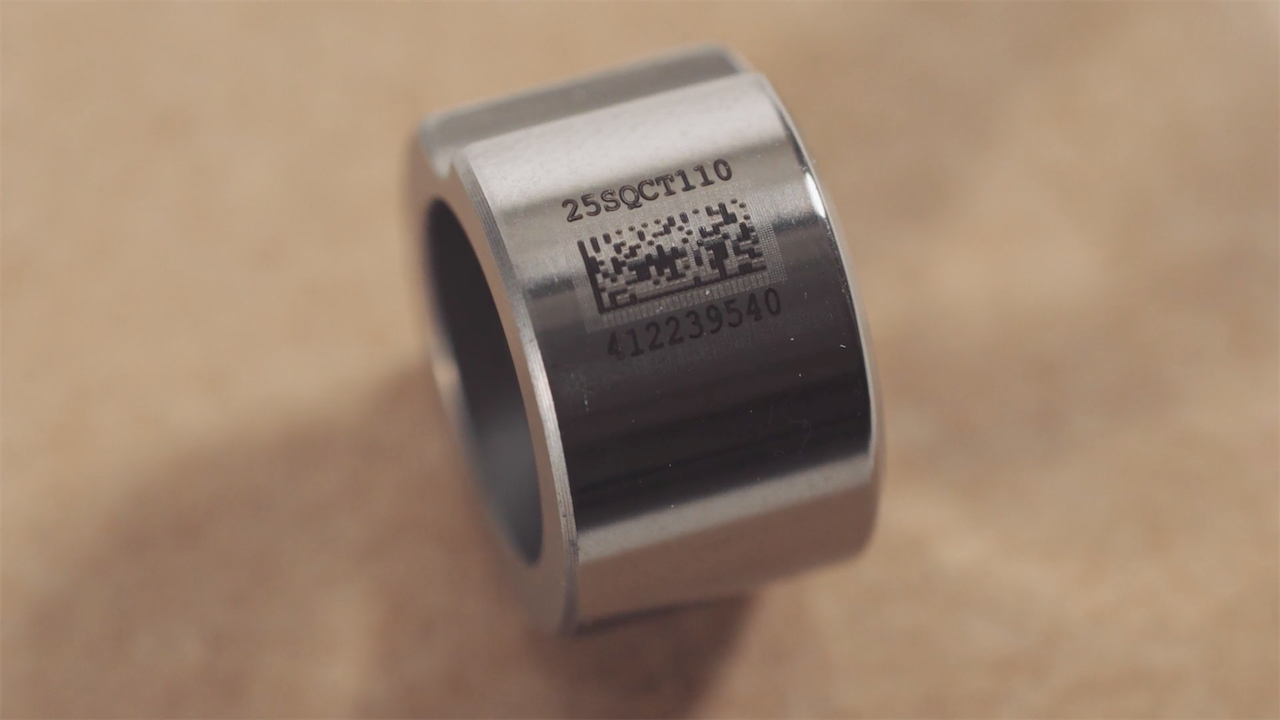
- Direct Part Marking (DPM), or direct marking, where Data Matrix barcodes are permanently inscribed onto solid surfaces using technologies like laser etching, pneumatically driven marking pins (dot peening), scribing engravers, and thermal printers. (Pictured below)

What makes the Data Matrix barcode unique?
Compared to other barcode symbologies, what makes Data Matrix barcodes unique is their ability to store large amounts of data in a small physical size.
Key benefits of Data Matrix vs. other barcode types
- Adaptable in physical size (the smallest being around 2.5 mm square) and supporting variable-length data content.
- Support for various character encoding, including all 256 ASCII characters, ISO characters, and EBCDIC characters.
- Omnidirectional reading capability, allowing users to scan them from any direction – especially useful in warehousing and retail point-of-sale environments.
- Its physical size and data capacity are independent of each other, allowing the choice of many different matrix sizes.
- Robust error correction capabilities and the ability to withstand up to 30% of damage, yet still be readable.
- Different error correction levels can be defined by varying the size of the symbol.
How to create a Data Matrix barcode
To create a Data Matrix barcode, you need software that encodes the supplied data into the pattern defined by the ISO/IEC 16022 international standard. There are multiple options, including barcode generator apps, online tools, and coding the generator yourself.
The process generally involves inputting the data you want to encode and selecting Data Matrix as the desired barcode type. The tool then generates a visual representation of the code, which can be downloaded or printed.
How to scan a Data Matrix barcode
Data Matrix barcodes can be scanned with camera-based mobile devices running software able to decode the symbology. For example, most industries use UTF-8 encoding—if your scanning software cannot recognize this and handle non-standard cases, its results may be unusable.
Scandit’s barcode scanning software supports Data Matrix codes and over 35 other symbologies. For Data Matrix barcodes specifically, the Scandit Barcode Scanner SDK:
- Speeds up the localization and decoding of Data Matrix codes, including square and rectangular symbols, and large symbols with perspective and non-linear distortions.
- Decodes inverse Data Matrix barcodes that use inverted colors.
- Identifies GS1 codes to signal that they contain GS1 data and includes a GS1 Parser API to translate data components into usable formats.
- Enables scanning of Data Matrix codes inscribed onto solid surfaces using DPM.
How to decode a Data Matrix barcode
If you’re building your own Data Matrix decoding method, the general steps are as follows.
Pre-requisites
The image of the Data Matrix barcode is captured and stored with a resolution high enough to distinguish its components.
Decoding steps
- Using the captured image, identify the finder pattern and quiet zones to distinguish the symbol from the background.
- Convert the image into a binary representation using thresholding, where pixels are set to a maximum value (usually 255 for white) or minimum (usually 0 for black) based on whether the corresponding image segment is above or below a given threshold value.
- Examine the timing pattern to estimate any perspective distortion and the version information to determine Data Matrix code’s size.
- Read and decode the data pattern using the given encoding scheme, usually ECC 200. In this scheme, a "light" cell typically represents a 0 and a "dark" cell represents a 1.
- Translate the data stream into an encoding scheme usable by your app. If the symbol’s scheme is unknown, you have two options:
- Send the raw data to the app.
- Convert the data from the data encoding used in the code to the encoding required by the app—this is usually UTF-8..
- If the data is encoded as “GS1” (the flag is set), decode the element strings and handle errors according to the GS1 guidelines. One approach is illustrated by the data processing flowchart in Section 2.2 of the GS1 DataMatrix guidelines.
- Send the results to the application for further processing or display.
The Scandit Barcode Scanner SDK implements these steps for you and provides additional features based on real-world development and production experience.
For example, adding a Data Matrix code reader to your app only requires two steps after setting up the Scandit software. The following instructions are based on the JavaScript sample app, "Barcode Capture Simple Sample":
First, enable the required symbologies, including Data Matrix.
settings.enableSymbologies([
Symbology.EAN13UPCA,
Symbology.DataMatrix,
Symbology.Code39,
Symbology.Code128,
]);After a barcode is decoded and recognized by the Scandit library, you can retrieve its data by implementing the Scandit listener interface.
barcodeCapture.addListener({
didScan: async (barcodeCaptureMode: BarcodeCapture, session: BarcodeCaptureSession) => {
// Disable the mode to avoid unwanted scan until the user closes the displayed result.
await barcodeCapture.setEnabled(false);
// Hide the viewfinder.
await barcodeCaptureOverlay.setViewfinder(null);
const barcode: Barcode | null = session.newlyRecognizedBarcode;
if (!barcode) {
return;
}
const symbology: SymbologyDescription = new SymbologyDescription(barcode.symbology);
showResultScanned: ${barcode.data ?? ""}\n(${symbology.readableName}));
},
});Here, the method extracts:
barcode.symbology—barcode symbology as an enumeration.barcode.data—barcode data as a UTF-8 string.symbology.readableName—human-readable name of the symbology.
How Scandit supports Data Matrix codes
The Scandit Barcode Scanner SDK is designed to meet the needs of real-world developers, including these features specific to Data Matrix codes:
- Extracting information in UTF-8 and/or raw data formats.
- The GS1 Parser API to automatically normalize and extract element strings into a human-readable format without worrying about encoding or delimiters. This includes tuning options, such as strict adherence to the ECC 200 standard, enabling GS1 extensions, and overriding the length of the Application Identifier string.
- Enabling and disabling of supported symbologies, including industry presets, to improve scanning performance.
- Extracting data from multiple barcodes simultaneously, with MatrixScan.
- Support for structured append by automatically extracting information across multiple symbols when this feature is set. When combined with MatrixScan, this returns data from all labels in one scan.
Scandit’s software supports all major operating systems, programming languages, and frameworks, including Native iOS, Native Android, JavaScript, Cordova, Xamarin and Xamarin.Forms, .NET (iOS, Android, and MAUI), React Native, Flutter, Capacitor, Titanium, IBM MobileFirst, SAP Fiori, and Oracle Xstore.
Light conditions can vary in warehouse and maintenance environments. Scandit’s scanning performance enables barcodes to be scanned and read accurately and quickly regardless of their material condition, distance away from the scanner, or varying light conditions.

Try the Scandit Barcode Scanner SDK
Evaluate our Data Matrix decoding with a 30-day free trial
)