Category: 2D Symbologies
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Micro QR codes are a smaller and simpler version of QR codes, made up of a square grid of dark and light boxes and one prominent square at the top-left corner. They are used for small items in retail, electronics, security, and manufacturing applications. They are similar to QR codes but physically smaller and carry less information.
This technical guide helps software developers build applications that create or decode Micro QR codes. We’ll explain how they work and answer common questions. We’ve also included a code sample demonstrating how to integrate Micro QR code scanning into your app.
What is a Micro QR code?
A Micro QR code is a smaller version of the QR code (“Quick response” code), used for spaces with limited room. It’s a two-dimensional barcode that stores data in a square grid of dark and light squares and can be read from any angle (left, right, top, or bottom).
Micro QR codes represent machine-readable data graphically, known as a data carrier. The data inside the carrier is known as the data structure, which is encoded in different formats that applications must know how to decode. Micro QR codes support alphanumeric, numeric, 8-bit binary, and kanji character sets.
Micro QR codes come in four sizes, storing up to 21 alphanumeric characters, 35 numeric digits, 15 bytes (120 bits), or nine kanji characters.
To scan a micro QR code, a device needs to run image processing, decoding, and error correction algorithms. Micro QR codes are commonly used for retail, website, business card, and electronic parts applications.
Micro QR codes were invented by DENSO Wave and approved as the JIS X 0510 standard in 2004. It is currently covered by the ISO/IEC 18004:2024 and AIM ISS QR Code standards.
Try the Scandit Barcode Scanner SDK
Evaluate our Micro QR code decoding with a 30-day free trial
How a Micro QR code works
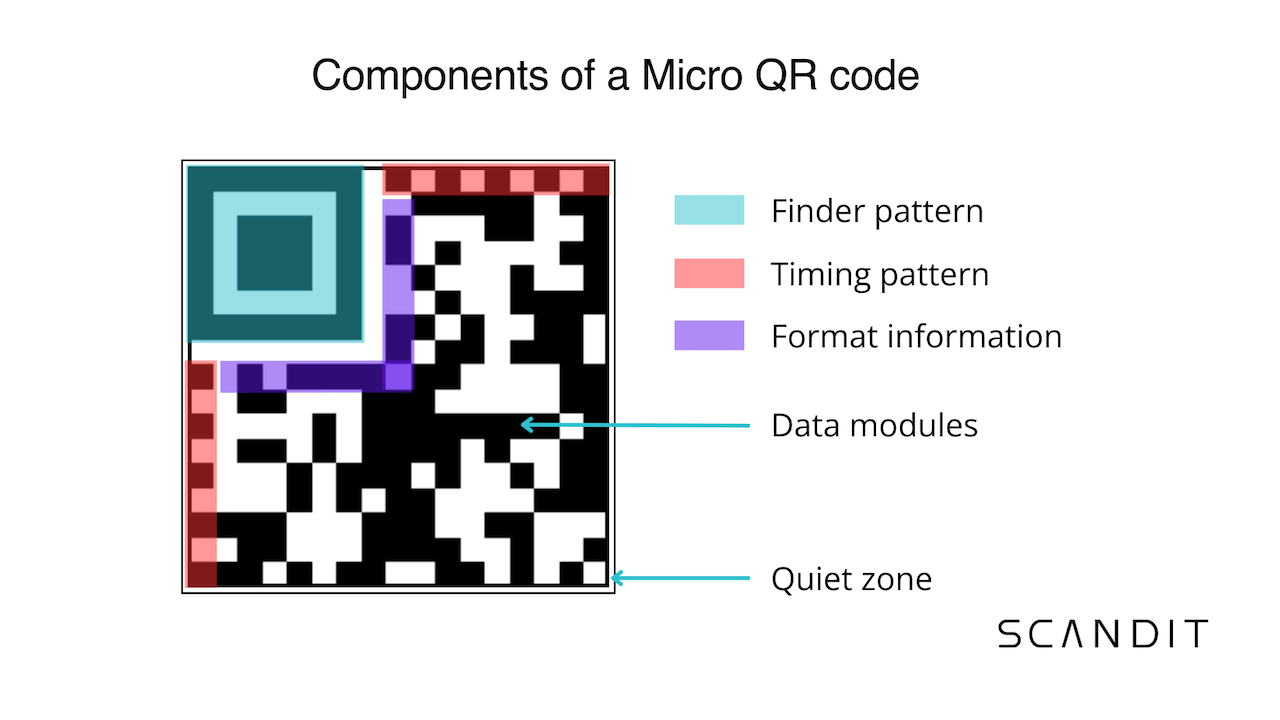
A Micro QR code symbol contains these components:
- Finder pattern: One large square at the top left corner to help scanners establish the position and orientation of the symbol.
- Timing pattern: Dotted lines running vertically along the left side and horizontally along the top of the symbol. These help barcode scanners determine the structure and orientation of the symbol’s data modules.
- Format information: Strips of squares beside the finder pattern that contain details about the symbol’s size, masking pattern (which elements are dark vs. light), and error correction level.
- Data modules: The grid of dark and light squares that stores the symbol’s information.
- Quiet zone: The white border around the symbol separating it from the background.
 What are the Micro QR code versions?
What are the Micro QR code versions?
Micro QR code versions range from M1 to M4, each with a different number of data modules that determine its data capacity and physical size. The smallest version, M1, has 11 modules while the largest, M4, has 17 modules.
Although their names are similar, the Rectangular Micro QR code (rMQR code) is not a variant of the Micro QR code. It is a specialized type of QR code, with similar features, but designed to fit in long, narrow spaces such as thin electronics parts or shipping labels.
How much data can a Micro QR code store?
Each Micro QR code version has a maximum data capacity according to the amount of data, character encoding scheme, and error correction level used.
The following table shows the storage sizes for Micro QR code versions at the lowest error correction level (L, with an approximate 7% data restoration rate):
Version | Module size | Maximum characters (alphanumeric) | Maximum characters (numeric) | Maximum characters (8-bit binary) | Maximum characters (Kanji) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
M1 | 11x11 | - | 5* | - | - |
M2 | 13x13 | 6 | 10 | - | - |
M3 | 15x15 | 14 | 23 | 9 | 6 |
M4 | 17x17 | 21 | 35 | 15 | 9 |
*Due to its size, M1 does not support any level of error correction | |||||
In comparison, the smallest QR code (version 1, with a 21x21 module size) supports up to 41 numeric characters, while the largest (version 40, 177x177) can hold up to 7,089 numeric characters.
What is the difference between static and dynamic Micro QR codes?
The data in static Micro QR codes can’t be changed after they’re created, while dynamic Micro QR codes allow data to be edited even after they have been created and printed.
How is data encoded in a Micro QR code symbol?
Micro QR codes support four encoding methods:
- Alphanumeric (digits 0 - 9; upper case letters A - Z; and these characters: space, $ % * + - . / :)
- Numeric (digits 0 – 9)
- 8-bit binary (characters from the ISO-8859-1 character set, or other application-specific character sets)
- Kanji (double-byte characters from the Shift JIS character set)
Micro QR code error correction
Micro QR code error correction uses the Reed-Solomon method, allowing barcode scanning software to recover data from poorly printed, obscured, or damaged labels. This method uses a polynomial operation to convert the original data into a unique set of points embedded into the Micro QR code’s symbol. Scanners can then use these points to rebuild the data.
Only versions M2 to M4 support error correction. There are three levels supported:
- L: 7% of data can be restored.
- M: 15% of data can be restored.
- Q: 25% of data can be restored (only supported by version M4).
When creating a Micro QR code, selecting the right level of error correction for the application is crucial, since higher levels need more space. For example, an M4 barcode with level Q error correction holds less data than an M3 barcode with level L error correction.
Where is a Micro QR code used?
Micro QR codes have many benefits of QR codes (fast to scan, encode structured or free-form payloads, and recoverable from errors), but are more suited for small spaces.
Application examples include:
- Small retail product labels: To carry data such as batch numbers, expiration dates, and product descriptions.
- Electronics: Affixed to small components, such as printed circuit boards, to hold tracking information, serial numbers, and manufacturing details.
- Security: Applied to ID cards and access passes to store encrypted employee information and access permissions.
- Healthcare: Used for medical devices, lab sample containers, and patient wristbands to store manufacturing information, test details, and medical history.
- Manufacturing: Printed on small parts and packaging to encode serial numbers, dates, and batch information.
What is the difference between a QR code and a Micro QR code?
Micro QR codes operate on the same basic principles as QR codes, such as encoding data graphically and working under any orientation, but there are notable differences.
The following table lists the differences between QR codes and Micro QR codes:
Feature | Micro QR code | QR code |
|---|---|---|
Size | Smaller size, from 11x11 to 17x17 modules | Larger size, from 21x21 to 177x177 modules |
Representative data capacity (in characters), comparing the versions with the largest sizes | Version M4: Alphanumeric: 21 Numeric: 35 Binary: 15 Kanji: 9 | Version 40: Alphanumeric: 4,296 Numeric: 7,089 Binary: 2,953 Kanji: 1,817 |
Error correction levels | Three levels (L, M, Q), with up to 25% error correction | Four levels (L, M, Q, H), with up to 30% error correction |
Symbol characteristics | Finder pattern: 1 large square in the top left corner | Finder pattern: 3 squares in the top left, top right, and bottom left corners |
Timing pattern: Multiple horizontal and vertical lines | Timing pattern: Multiple horizontal and vertical lines | |
Alignment pattern: None | Alignment pattern: 1 or more small squares | |
Quiet zone: two modules wide | Quiet zone: four modules wide | |
Ideal use cases | Small items with limited space (e.g. electronics, cosmetics, ID cards) | Larger items and scenarios requiring greater amounts of data (e.g. shipping labels, event tickets, links to landing pages) |
How to create a Micro QR code
To create a Micro QR code, you must use a software-based generator to encode your data into a matrix of dark and light modules defined by the Micro QR code standard. Once you find or develop a generator, the process is similar to this:
- Decide what data you want to encode and choose the right encoding scheme for your industry and use case.
- Encode the data and apply the Reed-Solomon error correction method.
- Render the data into the graphical data carrier symbol with proper quiet zones so it can be scanned reliably.
There are both commercial and free online Micro QR code generators available.
How to scan a Micro QR code
To scan a Micro QR code, you need a smart device with a camera running software designed to decode the symbology.
Scandit’s barcode scanning software supports Micro QR codes and over 35 other symbologies, including these features:
- Accelerated Micro QR code scanning under poor environmental conditions, long distances, and non-linear distortions.
- Simultaneous data extraction from multiple Micro QR codes within the field of view, with MatrixScan.
- Scanning Micro QR codes and text labels together, using Smart Label Capture.
How to decode a Micro QR code
If you’re building an application that needs to decode Micro QR codes, the general steps are as follows.
Pre-requisites
- An image of the Micro QR code is available to the app, with a high resolution to distinguish its components.
Decoding steps
- Use image thresholding to convert the image into a binary representation. This method sets pixels to maximum or minimum values based on whether image segments are above or below a given threshold (usually 255 for white and 0 for black).
- Identify the finder pattern and quiet zone to distinguish the Micro QR code symbol from its background.
- Determine the encoding mode (alphanumeric, numeric, 8-bit binary, kanji) by examining the symbol’s format information.
- Extract the bits from the data module, which are read from the bottom right to the bottom left, following a snaking path through each column.
- Decode symbols from the bits and handle errors using the Reed-Solomon error correction method.
- Translate the data into an encoding scheme understood by your app. If the Micro QR code’s scheme is unknown, you can send raw data to your app or convert it into a recognizable format. This is commonly UTF-8, but you should verify with the creator of the Micro QR code.
- Send the data to the app.
The enterprise-proven Scandit Barcode Scanner SDK implements all these decoding steps for you. It includes advanced features that help developers deploy faster and adapt Micro QR code scanning to any industry.
Adding Micro QR code support to your app only requires two steps after starting your free trial and setting up the Scandit software. The following instructions are based on the "Barcode Capture Simple Sample" application for the Scandit JavaScript Barcode Scanner SDK:
1. Enable the required symbologies, including Micro QR codes
settings.enableSymbologies([
Symbology.MicroQR,
Symbology.DataMatrix,
Symbology.EAN13UPCA,
]);2. On a successful barcode capture, retrieve its data by implementing the Scandit listener interface
barcodeCapture.addListener({
didScan: async (barcodeCaptureMode: BarcodeCapture, session: BarcodeCaptureSession) => {
// Disable the mode to avoid unwanted scan until the user closes the displayed result.
await barcodeCapture.setEnabled(false);
// Hide the viewfinder.
await barcodeCaptureOverlay.setViewfinder(null);
const barcode: Barcode | null = session.newlyRecognizedBarcode;
if (!barcode) {
return;
}
const symbology: SymbologyDescription = new SymbologyDescription(barcode.symbology);
showResultScanned: ${barcode.data ?? ""}\n(${symbology.readableName}));
},
});This method extracts:
barcode.symbology- barcode symbology as an enumeration.barcode.data- barcode data as a UTF-8 string.symbology.readableName- human-readable name of the symbology.
How Scandit supports Micro QR codes
The Scandit Barcode Scanner SDK meets the needs of real-world developers, including these features specific to Micro QR codes:
- Highly optimized scan and decode performance for Micro QR codes in a range of environments, including tiny barcodes, multiple barcodes, electronic shelf labels (ESL), color-inverted labels, and degraded conditions (low light, long distances, awkward scan angles)
- Normalization of all encoding schemes to UTF-8, if the data is convertible, or access to the raw data.
- Enabling and disabling of supported symbologies, including industry presets, to improve scanning performance.
The Scandit SDK supports all major operating systems, programming languages, and frameworks, including Native iOS, Native Android, JavaScript, Cordova, Xamarin and Xamarin.Forms, .NET (iOS, Android, and MAUI), React Native, Flutter, Capacitor, Titanium, IBM MobileFirst, SAP Fiori, and Oracle Xstore.
“Firstly, with Scandit every process is now happening in real-time. Second, store associates are going beyond agreed SLAs for receiving goods as it is faster and easier – resulting in superior stock accuracy. And third, we can complete all the omnichannel processes closer to the customer.”
Andrea Comi, Global Director, Digital and Technology DTC, VF Corporation

Try the Scandit Barcode Scanner SDK
Evaluate our Micro QR code decoding with a 30-day free trial.